Utilities Companies Adopt Cost-Effective 5G and 4G IoT Connectivity For Smart Meters
August 20, 2020
Story

To connect their smart meters, utility companies are moving from what they?ve traditionally used, mesh technology, toward 3GPP standardized 4G and 5G cellular.
To connect their smart meters, utility companies are moving away from what they’ve traditionally used, mesh technology such as Wi-SUN® with distributed access points, toward 3GPP standardized 4G and 5G cellular. This is because the price of 4G LTE modules and chipsets have dropped significantly now that LTE networks are universally available and volume pricing has come into play. While Wi-SUN technology may have been the best option for connecting utility meters in the past, today the advantages of cellular have upended this paradigm. It introduced a new economic environment in which cellular has become the better choice to connect smart utility meters: better in cost, scale, and efficiency.
Cost
In the early days of 4G, the cost of an LTE M2M module was approximately $100, and available from only one source. At that time, there were no unlimited data plans available from any of the carriers and 2G/3G technology was notoriously power hungry, requiring large, expensive batteries. Mesh technologies, such as Wi-SUN, were used because the technology was cheaper than cellular. There were no issues with respect to data plans, and power usage could be optimized well-enough for a specific smart meter use case.
With the advent of LTE-M, defined by 3GPP in Release 13 and created specifically for low power wide area (LPWA) networks for IoT, the landscape has changed entirely. Today there are more than a dozen companies developing LTE-M chipsets, and more than a dozen module makers using those chipsets, and there are a multitude of data plans offered by the major carriers to IoT companies, including utility providers, and MNOs/MVNOs, all working to drive costs down across the ecosystem. Highly efficient LTE-M technology also solved the power consumption issue.
Scale
While mesh technology is limited in its ability to scale, LTE-M has no such limitation and can scale with virtually no limit; a capability that will continue to drive down prices in the coming years. Mesh requires utility companies to deploy their own networks and bear all the burden of maintaining and upgrading those networks at an ever-increasing cost that drives the total cost of ownership up and up. Today, LTE-M is available at nearly 99% coverage in the USA from leading operators AT&T, T-Mobile, and Verizon. There is no longer any need for utility companies to build and maintain their own mesh networks.
Efficiency
Cities and other municipalities who are customers of utility companies, are now looking at more comprehensive smart city initiatives that include infrastructure, public safety, transportation, streetlights, parking meters, and more. This evolution creates an opportunity for utility companies to capture more revenue from their customers by expanding their services beyond smart metering to smart city services. Spending time developing and expanding business and increasing TAM (total available market) instead of spending money on developing infrastructure, modules and software, enables utility companies to create new revenue streams and increase efficiencies in the ever-expanding smart city market.
Monarch SiP: The Sequans Solution for Smart Meters
Sequans, together with Skyworks, have brought to market a solution for the smart meter market called Monarch SiP, an LTE-M connectivity module that was developed with utility meters in mind. Particularly, water and gas meters, which require specific packaging capabilities and a very high level of reliability due to their typically harsh and corrosive environments. Monarch SiP combines Sequans’ Monarch LTE-M chipset with the universal radio front end of Skyworks in the world’s smallest package that is ultra-low in power consumption, and ultra-high in reliability and coverage, resulting in an LTE-M connectivity solution that is ideal for water and gas smart meters.
Power Consumption
Sequans has achieved ultra-low power saving mode (PSM) power consumption of 1µA at rock bottom, which is the lowest in the industry and three times better than the nearest competitor. This means that in eDRX mode where the meter wakes up, for example, every 20 minutes, a Sequans device is able to sleep at this 1µA level for 19 minutes and 56 seconds (assuming 4 seconds of active time). This allows meter companies to scale down the size of their batteries significantly, reducing battery cost while offering longer battery life. Since many water and gas meters are expected to live 20 years in the field, they have traditionally carried sizeable and expensive batteries. But, using Monarch SiP, many of our customers have been able to reduce their battery size by half and in some cases even more.
A power consumption comparison between a Sequans module and a competitor module (claiming 3µA power consumption at rock bottom) has recently been conducted. In the figure below, the top section shows the power consumption of a Sequans’ Monarch GM01Q module and the bottom section shows the power consumption of a competitor’s module. The results show the Sequans device with average power consumption of 1.27µA while the competitor’s device shows an average of 20.4µA. (Note: the Monarch GM01Q module and the Monarch SiP module are identical in performance and software.)
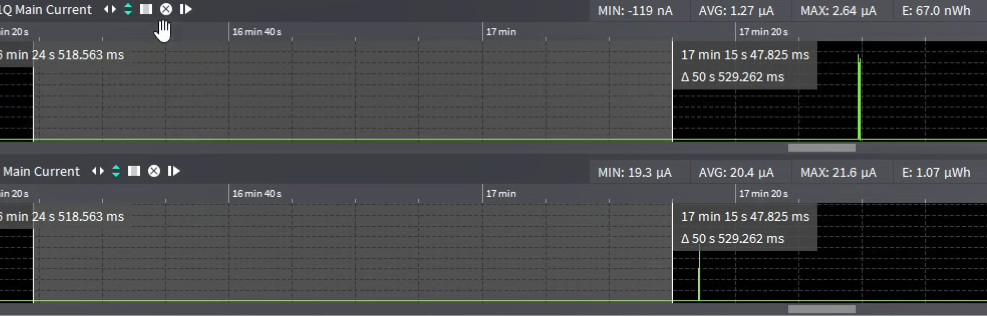
The power consumption comparison was also made using an eDRX cycle with a 5-minute interval. In the figure below, results show that the Monarch GM01Q device consumes half as much power as the competitor’s device. Even when the eDRX cycle interval is increased (a case not uncommon for meters and battery-operated devices), the Monarch GM01Q power consumption advantage is seen to be even more significant at 75% better than the competitor’s device.

Reliability
Monarch SiP is one of the most reliable solutions in the market today. Gas contains sulfur and water creates humidity, both of which have an adverse effect on standard modules that contain silver in the shielding. Monarch SiP is uniquely silver-free making it an ideal solution for the harsh environments present with gas and water meter installations. The lower corrosion rates enabled by Monarch SiP enable long-term deployments of 20 years or more, with fewer truck rolls. While it is true that metering companies can design and build their own protective technology to ensure no sulfur or humidity pockets form close to their devices, the use of Monarch SiP eliminates this added expense, which companies can then use for R&D or value-added services. Additionally, Monarch SiP can be purchased with an even higher reliability package option where certain pins are placed in strategic locations to eliminate potential issues of package warpage or loosening of the solder that mates the package balls to the PCB. The use of this package enables customers to reduce issues related to vibration; a distinct advantage over the alternative use of hard epoxy materials.
Coverage
Coverage is an important consideration for the metering industry since meters are not mobile and are usually located in deep indoor locations and sometimes at the cell edge where RF signals may be attenuated. Monarch SiP uses 23dBm transmission power, which reduces the need for repetition, retransmission, and can partially compensate for RF signal loss. Repetition and retransmission require that a system be awake for longer periods of time, reducing the life of battery-operated gas and water meters. In some cases, devices that don’t have 23dBm power at the cell edge will not be able to transmit even with repetitions and retransmissions. Monarch SiP with its 23dBm power capability provides superior coverage in deep indoor, buried, and cell-edge implementations.
Conclusion
Monarch SiPs are well suited for deployment in utility monitoring applications because of their small 8.8 mm x 10.8 mm x 0.95 mm size, low power consumption, high reliability, and competitive pricing that compares to most standard M2M modules. The devices have also been certified by multiple cellular operators, which allows the SiPs to be deployed in almost any geography.
About the Author
Nick Taluja leads Sequans' worldwide sales operations. In this role, he drives the formation and execution of Sequans global sales strategy that supports the company's overall business objectives. Taluja has extensive sales management experience having lived in North America, Europe and Asia and worked for American, European and Asian companies.
Prior to joining Sequans, Taluja led the sales organization for SK hynix, a leading supplier of DRAM and Flash memory solutions, as vice president for the Americas.
Previously, Taluja was with ST-Ericsson from 2007-2013, the former multinational supplier of wireless semiconductor products including LTE solutions, where he most recently led the Americas' sales and marketing organizations. Taluja has more than 20 years of sales, product marketing and business development experience, including having worked for Texas Instruments and TranSwitch, specifically in the areas of wireless and wireline communications and has co-authored three patents
in the field of near field communications (NFC). Nick holds an M.S. in electrical engineering and a B.S in computer engineering and mathematics from Kansas State University.




