Renesas Develops Automotive SoC Functional Safety Technologies for CNN Accelerator Cores and ASIL D Control
February 18, 2021
News
Renesas announced the development of processor technologies for automotive systems-on-chip (SoCs) used in applications such as advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving (AD) systems that aim to optimize both performance and power efficiency while supporting a high level of functional safety.
Renesas’ development announced includes: 1) A convolutional neural network (CNN) hardware accelerator core that delivers a combination of deep learning performance of 60.4 trillion operations per second (TOPS) and a power efficiency of 13.8 TOPS/W; 2) safety mechanisms for detection of and response to random hardware failures. This makes it possible to create a power efficient detection mechanism with a high failure detection rate; 3) A mechanism that allows software tasks with different safety levels to operate in parallel on the SoC without interfering with each other, thereby bolstering functional safety for ASIL D control. These technologies have been applied in the company’s latest R-Car V3U automotive SoC.
Renesas presented these achievements at the International Solid-State Circuits Conference 2021 (ISSCC 2021).
According to the company, applications such as next-generation ADAS and AD systems require deep learning performance of 60 TOPS or even 120 TOPS alongside power efficiency. In addition, since signal processing from object identification to the issuing of control instructions constitutes the bulk of the processing load in AD systems, achieving the functional safety equivalent to ASIL D – the strictest safety level defined in the ISO 26262 automotive safety standard – is an issue. Renesas has developed new technologies to meet these needs, including a hardware accelerator that delivers CNN processing performance with ideal power efficiency.
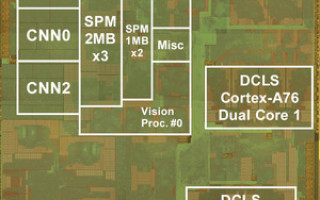
The technologies used in the R-Car V3U SoC are described below.
- Development of high-performance CNN hardware accelerator with suitable power efficiency
Renesas has developed a CNN hardware accelerator core with deep learning performance and implemented three such cores, in a high-density configuration, on the R-Car V3U. In addition, the R-Car V3U has 2 megabytes (MB) of dedicated memory per CNN accelerator core, for a total of 6 MB of memory. Per the company, this reduces data transfers between external DRAM and the CNN accelerator by more than 90 percent and achieved a CNN processing performance of 60.4 TOPS with ideal power efficiency of 13.8 TOPS/W (Note 1).
- Development of safety mechanisms for ASIL D systems capable of self-diagnosis
Renesas has developed safety mechanisms for fast detection of and response to random hardware failures occurring in the SoC overall. Both reduced power consumption and a high failure detection rate are achieved by combining safety mechanisms suited to specific target functions. The incorporation of these mechanisms into the R-Car V3U is expected to bring the majority of the SoC’s signal processing into achieving the ASIL D metrics. An SoC that satisfies the ASIL D metrics is capable of independent self-diagnosis, and this reduces the complexity of fault tolerant design in an AD system.
- Development of a support mechanism for freedom from interference (FFI) between software tasks
Renesas has developed an FFI support mechanism that monitors all data flowing through interconnects in the SoC and blocks unauthorized access between tasks. This enables FFI between all tasks operating on the SoC, making it possible to realize an SoC for ASIL D applications capable of managing object identification, sensor fusion with radar or LiDAR, route planning, and issuing of control instructions with a single chip.
Note 1) The performance of the CNN hardware accelerator was measured on an optimized network.
For more information, visit: renesas.com




