Unlocking the Full Potential of Edge Workload Consolidation
July 06, 2021
Blog
It all begins by optimizing system configurations.
Embedded processor cores and expenses incurred are two variables that are indirectly proportional: A higher number of embedded processor cores results in reduced costs as the cores begin consolidating the workload by allocating the tasks to a single edge computing platform. While this cost-efficient measure successfully causes a decrease in the overall number of distributed embedded systems, it can only be achieved by accurately balancing out the computing cores and their respective virtual machines. This is where computer-on-modules come in to play: When paired with real-time virtual machines, Computer-on Modules (COMs) help designers realize this balance proficiently.
With technology advancing at an increasingly rapid pace, humans are becoming more reliant than ever on systems embedded in devices, machines, robots, vehicles, and machinery that are now trusted with the task of juggling a growing number of responsibilities. Accordingly, because of their ability to automate the workload in an efficient manner, these embedded systems are no longer simply managing a given application as they used to in the past; rather, they are now also acting as dynamic and complex channels of communication. For this reason, OEMs have to protect the information transmitted by assuring confidentiality and security especially with regards to IP manipulation and theft.
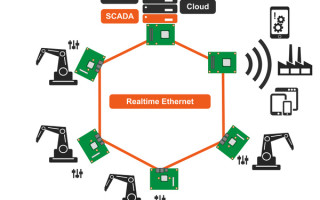
That said, one innovative idea is to execute the individual functions in enclosed containers located above the host operating system in order to ensure clearly defined access to these functions. Nevertheless, this proves to be imperfect when it comes to numerous applications in different kinds of industries that rely on a real-time system operating synchronously with other systems communicating in real time. In fact, the systems are associated together in real time through Time Sensitive Networking (TSN) or TSN over 10BaseT1L all the way up to the decentralized sensor or actuator, thus allowing for a consistent and smooth communication.
Large plants in general, and the process industry more specifically, stand to benefit the most from IP-based real-time networking as the two wire IP protocol has proven effective even with devices that are kilometers away. In other words, everything can be linked together through IP thereby ensuring uninterrupted transmissions in real time. Furthermore, the lloT edge servers also have access to the info retrieved from these systems, which can easily be made serviceable to big data analytics via special containers. In fact, analytics these days are mostly conducted locally as users are relying less and less on central clouds for storage. However, real-time based applications that should not be affected by other computing processes are incompatible with such containers. In this case, appropriate real-time hypervisor technology is needed, such as the RTS hypervisor from Real-Time Systems—already available at congatec as a function-validated standard option for specific COMs. For such setups, multi-core processors are particularly advantageous given the fact that multiple cores can be customized in numerous different ways. More specifically, every core has the ability to operate its virtual machine, consisting of an OS that can boot autonomously. This arrangement is also effective with dual-core systems. Hence, by investing in designs that are based on COMs, OEMs can always adjust the number of cores as the consolidation advances and runs the embedded system successfully by substituting the modules whenever they need to be replaced.
Development Kits for Workload Consolidation
The user-friendly workload consolidation kit developed by Congatec and Real-Time Systems helps users avoid difficulties when first getting introduced to modular edge servers. These ready-for-production Intel-certified kits are customized to cater to the needs of the latest multitasking autonomous vehicles and vision-based collaborative robot and automation controls. When used with a congatec COM Express Type 6 module consisting of an Intel® Xeon® E2 processor and three virtual machines, the ready-to-use platform has the capacity to reload a system application while allowing the real-time application to continue functioning on another virtual machine, unaffected. Rest assured: You could never get away with such a feat on a Windows-hosted hypervisor or container!
Compatibility with Time Sensitive Networking
Because real-time processing is becoming increasingly important in tactile Internet contexts due to 5G technologies and 10+ GbE networks, developers have also been hard at work ensuring that the kit supports Time Sensitive Networking. Time Aware Shaping (TAS), virtual LANs over Ethernet (IEEE 802.1q), and real-time synchronization via the Precision Time Protocol (PTP) are just some of the many standards that TSN technology complies with. The Precision Time Protocol is in charge of managing the coordination between the nodes, based on a time setting determined by a master. The clock of each slave guarantees high-precision synchronization well-defined in a two-digit nanosecond interval. Time-stamped packets are then issued according to the readings on these clocks. This allows the PTP networks to therefore adjust to the same level of precision. As a result, supplementary dedicated hardware or proprietary applications are not required in the case of a 1219 Intel Ethernet interface since clock synchronization is hinged solely on this fundamental element. The real-time workload consolidation starter set can now be acquired either from congatec or the Intel marketplace.
Caption 1: With cores becoming more widespread, now engineers can adopt the cost-effective measure of decreasing the number of distributed embedded systems by allocating the tasks to a single edge computing platform instead.

Caption 2: Starter kits for real-time workload consolidation are now available at congatec and include an Intel® Xeon® E2 processor-based COM Express Type 6 module as well as an RTS hypervisor from Real-Time Systems.

Caption 3: System consolidation is useful for producing cells that have numerous formerly decentralized robot controllers.




