Home Security and Health Care Using Wi-Fi Motion Detection
November 19, 2019
Story

Since its introduction in 1999, Wi-Fi has become ubiquitous. According to Wi-Fi Alliance, the 30 billionth device was shipped in 2019, just 20 years after the first.
Since its introduction in 1999, Wi-Fi has become ubiquitous. According to Wi-Fi Alliance, the 30 billionth device was shipped in 2019, just 20 years after the first. Not surprisingly, Wi-Fi is now found everywhere, with new applications being developed to serve new use cases across all market segments including residential, enterprise, and the IoT. One particularly innovative application of Wi-Fi technology, which may not be immediately apparent but has become possible thanks to developments in the way the technology is used, is motion detection.
Simply put, the propagation characteristics of Wi-Fi radio wave signals can now be used to detect the presence, motion, and activity of people. This can include people entering, exiting, or moving within a defined area such as a room. The ability to detect motion using Wi-Fi is ushering in a new set of use cases and applications, creating new categories of services and business models based on motion detection that can, in many cases, be applied anywhere Wi-Fi exists today.
Motion Detection Use Cases
Some compelling use cases for Wi-Fi based motion detection are emerging in many markets, including residential, health care, and enterprise.
|
Application |
Use Cases |
|
Residential |
Home security - intrusion alerts |
|
Automatically detect when cleaning or home repair staff arrive and depart |
|
|
Health Care |
Detect when in-home care personnel arrive or if an elderly person remains stationery for an extended period of time. |
|
Smart Home and Building |
Motion based HVAC and lighting control |
KPIs for Motion Detection
Several key performance indicators are critical for motion detection and are no less relevant for Wi-Fi based motion detection. Some of the key indicators are:
- Accuracy: The ability to determine with a high level of confidence the presence of a person entering or leaving an area while minimizing false positives. This puts greater importance on having good Wi-Fi coverage around the home, in order to avoid dead spots where detection may not be possible.
- Precision: The ability to distinguish between different movement patterns, such as walking, falling, or breathing, for instance.
- Speed: Detection needs to be fast and timely. Any security action needs to be detected in seconds, not minutes.
Wi-Fi is the fundamental building block
While disturbances in the field of most forms of radio frequency (RF) technologies can be used to detect motion, implementing it would typically require dedicated hardware. Conversely, in most cases no additional or specialized hardware is required to support motion detection using Wi-Fi. Furthermore, the widespread use of Wi-Fi makes it the ideal platform for implementing motion detection as an ‘over the top’ service.
Wi-Fi motion detection works due to the way that 2.4GHz and 5GHz RF radio waves propagate and react to stationary and moving objects in their operating environment. Every signal path exhibits a unique signature as it travels through the medium (or channel), changing slightly as it is absorbed or reflected by objects. Every device that receives a Wi-Fi signal provides feedback to the source of the signal; the access point (AP), router or gateway (GW). This feedback contains information about the channel’s characteristics, in wireless communications this is normally referred to as the Channel State Information (CSI) and it contains information that allows the transmitter to optimize its operation based on what the receiver ‘sees’.
The AP, router or GW analyzes the CSI data, to identify patterns that describe changes in the channel. More advanced algorithms can then determine if the reported disruptions are caused by someone entering or moving within a Wi-Fi field. Importantly, RF propagation delays and angles can also be calculated from this information, which provides the means to pinpoint the location of the object (or person).A visual representation of this CSI, plotted over time in the frequency domain, is shown in Figure 1. Motion events are detected by recognizing disturbance in the channel, as shown in Figure 2.
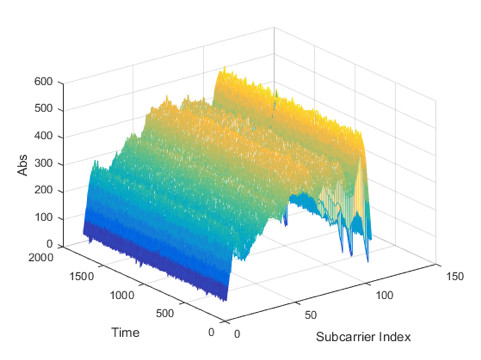
Figure 1. Channel Information across frequency and time

Figure 2. Motion events in a channel subcarrier
While the AP or GW will process this data locally in order to optimize its own operations, it can also grant access to the CSI data to a trusted 3rd party application who would use software algorithms to identify movement. Depending on the type of motion detection solution, these algorithms may run locally on the AP/GW, or remotely on a cloud platform.
High order MIMO - improving motion detection performance
Although it is realized through software, Wi-Fi motion detection is enabled by the hardware. Several factors can dramatically improve the KPIs of accuracy, precision, and speed of motion detection, all of which rely on good performance being provided by the underlying hardware platform.
MIMO (Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output) is a proven technology that significantly increases Wi-Fi performance, coverage and usable bandwidth in all environments. With MIMO, a multi-antenna GW or AP sends and receives data and channel information across multiple streams to client devices.
Because of the reflective and refractive properties of any environment, transmitted radio waves bounce off walls, objects, and people, which creates a multi-path transmission, as represented in Figure 3.MIMO leverages multi-path, which improves range, coverage, and speed. To illustrate how this is achieved in practice, consider Quantenna’s high order 8-stream MIMO device, which delivers more than 2x improvement in speed than a 4-stream device. MIMO is also the foundation for beamforming, which is a technique used to improve radio performance by focusing the RF energy towards the client(s) and thereby improving range and performance. Beamforming further improves the range that can be achieved, which is critical in this scenario because motion detection is not effective without adequate Wi-Fi coverage. Higher order MIMO based on Quantenna’s chipset also delivers greater insights into the multipath environment, thanks to the more detailed CSI data the chipset produces. The result is even better motion detection performance.

Figure 3. A representation of Multipath transmission using MIMO
In practice, the channel information is converted by the Wi-Fi chipset from RF energy into digital bits, for subsequent processing. The more bits used and made available to motion detection software, the higher the resolution. A chipset with 16 or even 12-bits CSI data as opposed to 8-bits will result in greater motion accuracy. Also, higher channel bandwidths will improve accuracy. As a result, the bandwidths supported by the Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 6 standards improves not only Wi-Fi throughput, but also motion detection accuracy. For example, simply doubling the Wi-Fi channel bandwidth from 40MHz to 80MHz can improve motion location accuracy by 40%.
AI in motion
A growing number of AP/GW manufacturers are now delivering advanced motion detection services based on Quantenna’s expertise in developing MIMO and Multi-user MIMO (MU-MIMO) chipsets. While the basic premise of Wi-Fi based motion detection is simple, delivering the accuracy, precision and speed needed to make it practical is a challenge few chipset manufacturers are able to address. The application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is adding a higher level of analysis, enabling greater detail and even higher reliability.
Detecting disturbances in RF energy is now a proven and effective method of implementing motion detection, as demonstrated by the growing number of partners working with Quantenna. Access to the rich CSI data Quantenna’s technology enables is bringing MIMO and AI together in exciting new ways.
Wi-Fi continues to evolve and is no longer just a wireless networking technology. Wi-Fi motion detection has become a practical, cost-effective technology that addresses real needs in residential security, health care, and enterprise applications. As Wi-Fi performance continues to increase with technologies such as MIMO, beam-forming, and high bandwidth operation, Wi-Fi motion detection performance also benefits.




